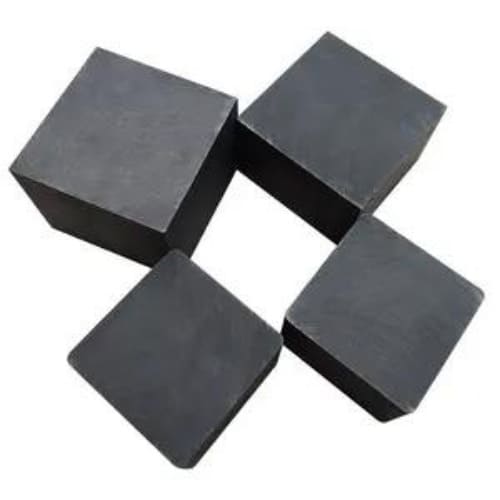
Graphite Block

Graphite Block
Purity: ≥99%
Graphite Block is a solid carbon material known for its exceptional thermal resistance and electrical conductivity. Made from natural or synthetic graphite, these blocks are engineered under high temperatures and pressures to achieve outstanding strength and durability. They are widely used in high-temperature environments such as metallurgical furnaces, chemical reactors, and heat exchangers. With high density, good machinability, and the ability to be produced in various shapes like rectangular, circular, or trapezoidal, graphite blocks support custom designs for specific industrial needs. We offer molded, high-purity, and isostatic graphite blocks, with maximum sizes reaching up to 3050 mm in length, 1000 mm in width, and 600 mm in height, meeting demanding applications across metallurgy, energy, and chemical industries.
Or email us at sales@heegermaterials.com.Graphite Block Data Sheet
| Reference Code | HM2594 |
| Purity | ≥99.9% |
| Color | Dark Gray to Black |
| Chemical Formula | C |
| Material Grades | Natural Graphite, Synthetic Graphite, Specialty Graphite, Composites Graphite |
| Density | 1.7–1.92 g/cm³ |
| Maximum Operating Temperature | Up to 3000°C (in inert atmosphere) |
| Thermal Conductivity | 100–200 W/m·K |
Graphite Block Description
Graphite Block is crafted from high-quality carbon materials and offers remarkable performance in extreme temperatures and harsh environments. Known for its excellent thermal stability, high electrical conductivity, and low thermal expansion, graphite block is commonly used in metallurgy, chemical processing, and energy industries. It can be precisely machined into different shapes and sizes, supporting a wide range of custom applications like furnace linings, casting molds, and heat exchangers. Available in molded, high-purity, and isostatic grades, graphite blocks provide reliable solutions where strength, precision, and resistance to thermal shock are essential.
Graphite Block Specifications
| Items | Unit | Value | |
| Grain Size | mm | 0.045-4 | |
| Bulk Density | g/cm3 | 1.65-1.95 | |
| Resistivity | μΩ•m | 8.0-11.0 | |
| Bending Strength | Mpa | 18-55 | |
| Compressive Strength | Mpa | 36-100 | |
| The Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (CTE) | ×10-6/ ℃ | 2.9-3.0 | |
| Ash | % | 0.1-0.3 | |
| Square | Length | mm | ≤3050 |
| Width | mm | ≤1000 | |
| Height | mm | ≤600 | |
| Products can be customized according to order requirements or specific drawings. | |||
Graphite Block Features
- Exceptional High-Temperature Resistance: Graphite block can withstand extremely high temperatures, with a melting point around 3850℃ and boiling point near 4250℃, maintaining stability even under intense heat conditions.
- Outstanding Thermal Shock Resistance: With a low thermal expansion coefficient, graphite blocks handle rapid temperature changes without cracking, ensuring durability in extreme environments.
- Superior Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: Graphite blocks deliver excellent heat and electrical transfer, outperforming stainless steel by four times in conductivity and far exceeding most non-metallic materials.
- Excellent Lubricity: Featuring a very low friction coefficient, graphite blocks provide smooth surface performance similar to molybdenum disulfide, enhancing their wear resistance.
- Strong Chemical Stability: At room temperature, graphite blocks resist corrosion from acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, maintaining structural integrity over time.
Graphite Block Applications
- Steelmaking Electrodes: Graphite blocks are machined into electrodes for electric arc furnaces (EAF), conducting electricity to melt scrap metal into molten steel with high efficiency.
- Furnace Insulation Material: Used as thermal insulation in metallurgical furnaces, graphite furnaces, and silicon carbide furnaces, helping control temperature and minimize heat loss.
- Heating Elements: Serve as heating sources in high-temperature industrial furnaces, maintaining stable heat even above 2000°C for processes like material synthesis and treatment.
- EDM Electrodes: Machined into electrodes for electrical discharge machining (EDM), enabling high-precision shaping of hard metals with excellent durability and wear resistance.
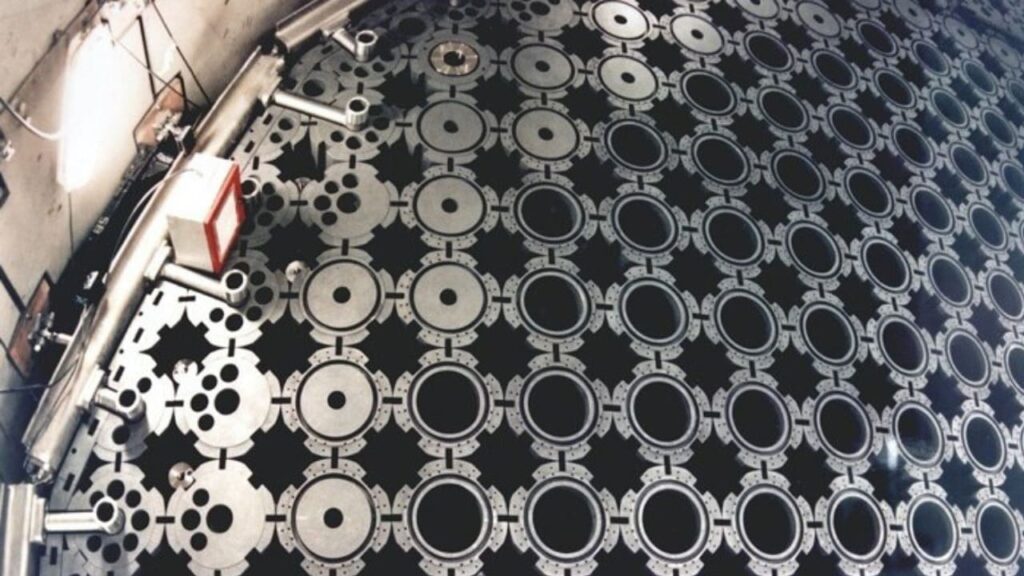
- Nuclear Reactor Moderator: Acts as a neutron moderator in nuclear reactors, slowing down neutrons to ensure a stable and controlled fission reaction for safe energy generation.
Graphite Material Properties
Graphite Material Grades
Natural graphite is classified into three primary types: amorphous graphite, flake graphite, and vein (lump) graphite. Each type has distinct characteristics and suits different industrial needs.
| Graphite Type | Introduction | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Amorphous Graphite | Microcrystalline graphite from metamorphosed coal seams; dull appearance and soft texture. | – Carbon content: 60–85% – Fine particle size – Good thermal conductivity – Moderate electrical conductivity – Good lubricating properties |
| Flake Graphite | Layered graphite formed in metamorphic rocks; shiny with metallic luster. | – Carbon content: 85–99% – Excellent thermal conductivity – High electrical conductivity – Strong lubricity – Stable in chemical environments |
| Vein (Lump) Graphite | Hydrothermally formed graphite with the highest purity and conductivity. | – Carbon content: 90–99% – Exceptional thermal conductivity – Very high electrical conductivity – Superior oxidation resistance – Excellent chemical stability |
Synthetic graphite is produced through the high-temperature treatment of carbonaceous materials. It offers more controlled properties compared to natural graphite, such as higher purity, better uniformity, and specific performance advantages for different industrial applications. Common types include biographite, die-molded graphite, extruded graphite, isostatic graphite, and vibration-molded graphite.
| Graphite Type | Introduction | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Biographite | Derived from biological materials through carbonization. | – Carbon content: 80–95% – Moderate thermal and electrical conductivity – Porous structure, good for filtration – Resistant to acids and bases |
| Die-Molded Graphite | Compacted carbon powders molded and graphitized. | – High density and strength – Excellent electrical conductivity – Chemically inert – Highly machinable |
| Extruded Graphite | Extruded carbon material with directional grain structure. | – High carbon content >99% – Good conductivity – Anisotropic properties – Moderate wear resistance |
| Isostatic Graphite | Produced by isostatic pressing for uniform properties. | – Ultra-high purity >99.99% – Isotropic strength – Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity – Fine grain structure |
| Vibration-Molded Graphite | Graphite formed by vibration compaction. | – High carbon content >99% – Good electrical conductivity – Durable with high compressive strength – Machinable into large parts |
Specialty graphite encompasses a wide range of engineered graphite materials designed to meet the demanding requirements of various industries. Each grade is uniquely processed or modified to enhance specific properties such as thermal conductivity, chemical resistance, structural strength, or electrical performance. These materials are critical across fields like energy storage, electrical discharge machining, nuclear technology, and high-temperature processing. Whether achieved through purification, impregnation, or advanced deposition techniques, specialty graphite grades offer targeted solutions where ordinary graphite would not suffice.
| Grade | Key Properties | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Battery-Grade Graphite | High purity (>99.95%), electrochemical stability, low surface area, spherical/flake particles (5–20 μm) | Lithium-ion batteries, energy storage systems |
| EDM Graphite | Fine grain (2–10 μm), high electrical conductivity, lightweight, erosion resistance, thermal conductivity | Electrical discharge machining (EDM) |
| Flexible Graphite | Highly flexible, thermal conductivity (150–300 W/m·K), chemical resistance, compressibility, wide temp range | Gaskets, seals, EMI shielding, thermal management |
| Metal-Impregnated Graphite | Enhanced thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, wear resistance | Bearings, seals, chemical processing equipment |
| Nuclear-Grade Graphite | High density (>1.70 g/cm³), low neutron absorption, thermal stability, radiation resistance, low porosity | Nuclear reactors (moderators, reflectors, shielding) |
| Pyrolytic Graphite | Highly anisotropic, in-plane conductivity, EMI shielding, chemical resistance, high density (≈2.20 g/cm³) | Electronics, aerospace, medical devices |
| Refractory Graphite | Abrasion and thermal shock resistance, chemical stability, oxidation resistance (coated), low thermal expansion | Metallurgy, ceramic industry, chemical reactors |
| Resin-Impregnated Graphite | Chemical resistance, improved strength, reduced porosity, oxidation resistance, lower conductivity | Pumps, mechanical seals, chemical handling equipment |
Graphite composites combine graphite with other materials like carbon, fibers, resins, or metals to enhance and balance their properties for specific high-performance applications. These composites retain graphite’s natural benefits such as lubricity, conductivity, and thermal stability while improving strength, wear resistance, or structural rigidity. Widely used across industries like aerospace, metallurgy, electronics, and chemical processing, graphite composites offer excellent solutions for demanding environments where traditional materials may fail.
| Property | Carbon-Graphite | Graphite-Fiber Composites |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | High, effective in high-friction applications | Good, with strong fatigue and impact resistance |
| Strength | High strength and rigidity | Exceptional tensile strength and high stiffness |
| Density | Lightweight due to low density | Very low density for critical weight reduction |
| Thermal Stability | Operates up to 3000°C in inert environments | Maintains integrity at high temperatures |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate to high, depending on constituents | High, enabling excellent heat dissipation |
| Electrical Conductivity | Good, suitable for EDM and electrodes | Moderate, useful for EMI shielding |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and organic solvents | Inert to most chemicals, moisture, and UV |
| Friction Properties | Self-lubricating, low friction even at extreme temperatures | High fatigue resistance, low thermal expansion |
| Oxidation Resistance | Limited, but can be enhanced with coatings | Stable in non-oxidizing environments |
| Applications | Metallurgy, EDM electrodes, high-temperature parts | Aerospace, structural composites, electronics |
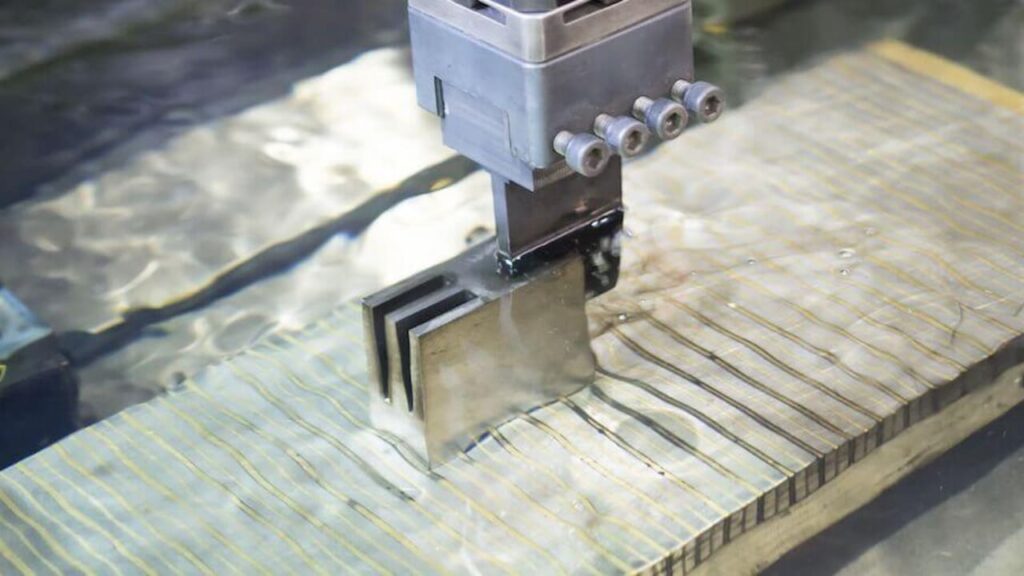
Graphite Ceramic Machining
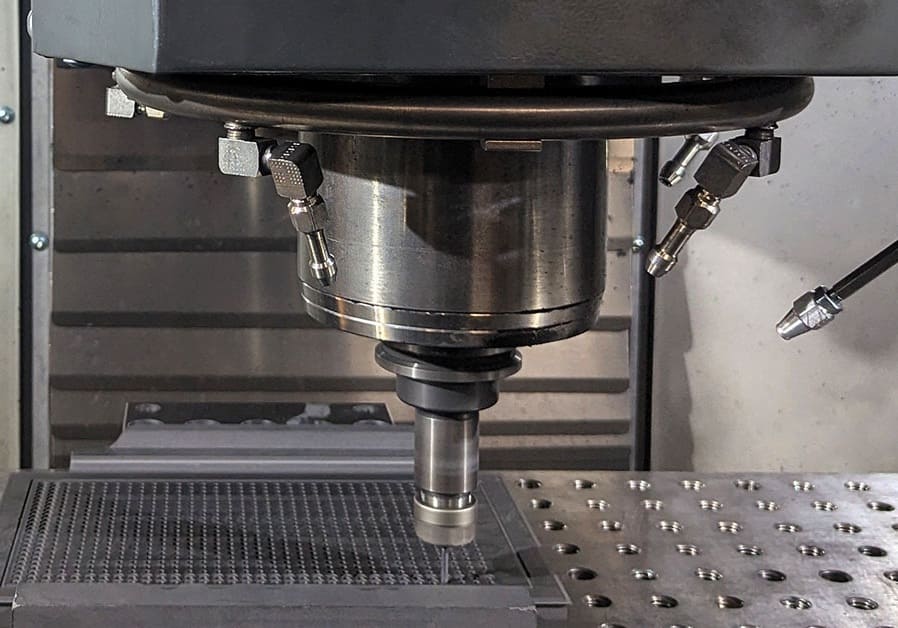

Graphite is a synthetic ceramic material made from crystalline carbon, offering exceptional thermal conductivity, high thermal resistance, low porosity, and stability at extreme temperatures. These properties make it essential for high-heat applications like casting, metallurgy, and electronics. However, machining graphite requires specialized techniques due to its unique characteristics: it is brittle and can produce fine particles and fissures during processing. Graphite does not deform under cutting forces like metals, demanding precise handling to maintain dimensional accuracy and surface integrity. Common machining methods include:
- CNC Machining: Computer-controlled drilling, milling, and grinding are widely used for creating complex graphite parts with tight tolerances.
- Diamond Grinding: Diamond tools are applied to achieve smooth finishes and precise shapes while minimizing particle generation.
- Sawing: Specialized saws are used for cutting graphite blocks into specific sizes or rough shapes before finer machining.
- Drilling: Custom graphite drilling requires careful speed and feed control to avoid cracks and achieve clean holes.
- Milling: High-speed milling with carbide or diamond-coated tools is utilized to produce detailed profiles and cavities.
- Surface Finishing: After primary shaping, additional grinding or polishing ensures the required surface finish for technical applications.
Graphite Ceramic Packaging
Graphite ceramic products are typically packaged in vacuum-sealed bags to prevent moisture or contamination and wrapped with foam to cushion vibrations and impacts during transport, ensuring the quality of products in their original condition.

Download
Get A Quote
We will check and get back to you in 24 hours.